Starlink beta test at the Conrad Observatory
by R. Leonhardt1. Introduction
Starlink is a satellite network, maintained by the SpaceX company, which should provide global Internet access in the future. A beta test has started in 2020. In 2021 I applied as beta tester for the then available system in mid latitudes. As a geophysical observer I am interested in whether such system can assist us in broadcasting our open earth observation data particularly from remote locations and whether the bandwith is suitable for remote operations and maintenance.
Geophysical data from seismometers, geomagnetic sensors, meteorological stations and many other related disciplines are often obtained from remote locations. Detailed analysis and interpretation of such data needs to be conducted near real time in order to facilitate in time hazard warnings. Data transmission is usually a significant problem. When needing remote control features bandwidth becomes essential. The Starlink antenna might provide a solution for such problems.2. Installation and test setup
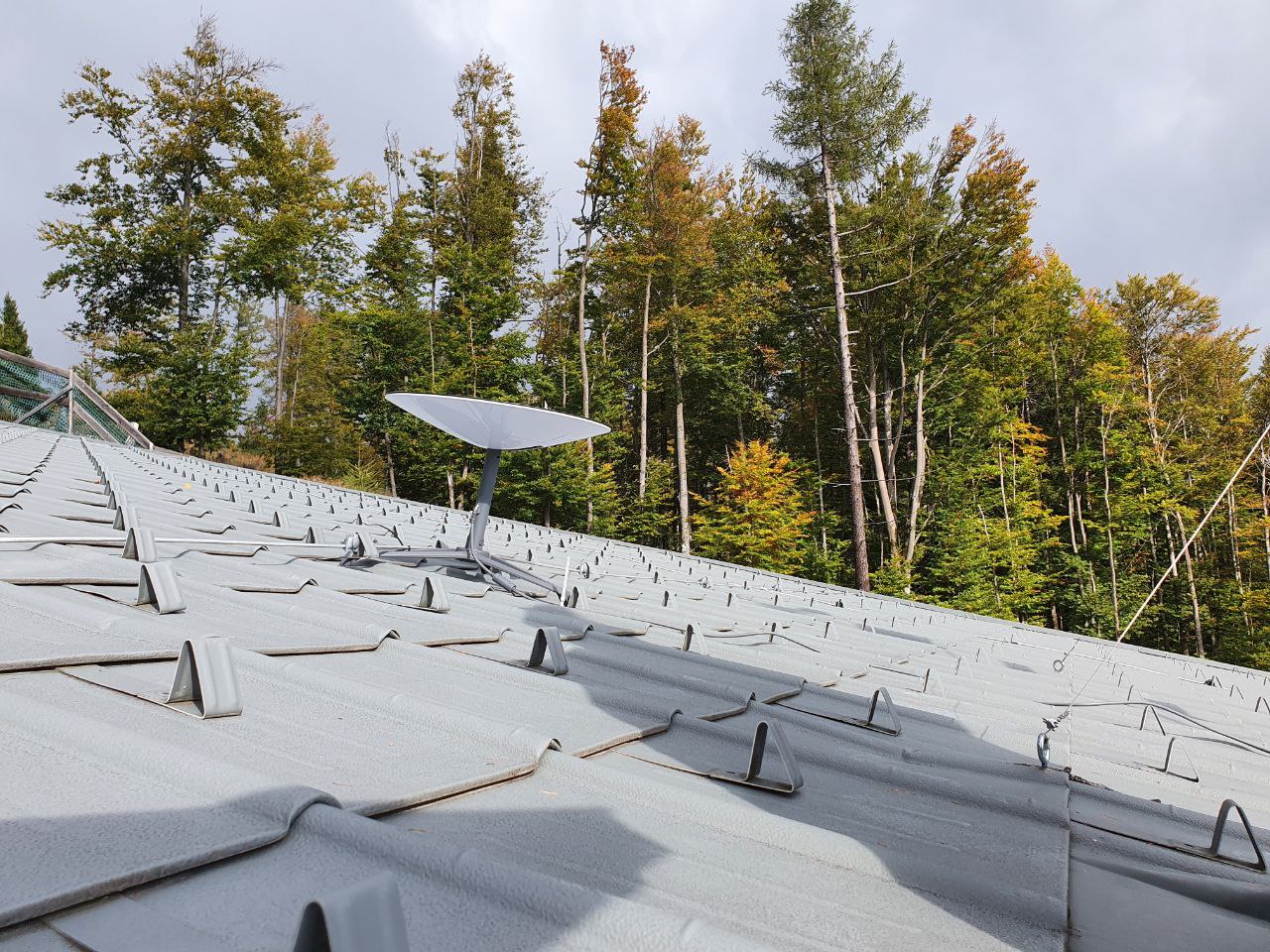
For the beta test the Starlink system is installed at the Conrad Observatory 50 km south west of Vienna, Austria. The antenna is mounted on the roof of the geomagnetic observatory with a relatively good but not perfect hemispherical view. During installation in September 2021 the Starlink app which contains a site testing facility, indicated an “improvable” location with proposed interruptions every 5 minutes. The antenna was installed with the standard tripod, which could be fixed at all three positions on the obervatories roof which has a tilt of 20 degree. As the antenna can compensate angles of up to 40 degree, this is a reasonable setup. A raspberry pi 4 is connected via WLAN provided by the Starlink router. The raspberry is used to perform the tests listed below.
3. Recorded time series
3.1. Bandwidth and latency
In order to permanently monitor band width and latency we are using the speedtest-cli application for linux. The speedtest is performed every 5 minutes by a scheduled job. Results are stored and archived on the raspberry. For analysis we are calculating hourly means of Download speed, Upload speed and latency. This values are stored in a database and shown in the first figure.
3.2. Data gaps and downtime
To get information about eventual downtimes and network interruptions, we installed a serial temperature sensor on the raspberry. The sensor is sampling every second and publishes this data directly using MQTT and a quality of service level 0. This means data is published as is without any memory. Another machine in Vienna is subscribing to this data stream and recording this data. We are analyzing the received data stream for the amount of gaps (in seconds) and the average duration of these gaps within hourly data blocks.
3.3. Dependency on precipitation and snow
The third plot shows meteorological data obtained about 500m away from the antenna location (and 50m below). Also not perfectly representative for the antenna position, those values are obtained close enough to be a good estimate.
3.4. Geomagnetic activity
Geomagetic activity is usually connected to currents in the ionosphere. The k index is calculated from local geomagnetic variations at the Conrad Observatory using the FMI method (checkout Kp for a global index at GFZ).
3.5. Temperature and humidity
Finally, we provide information on temperature and humidity variation measured at the same position as snow height and precipitation.
4. Results and discussion
The installation procedure is very simple. After plugging in, the Starlink system performs all further steps almost automatically. Using a cell phone with installed Starlink app, connected to the WLAN provided by the Starlink router, will help you during initial installation. When initially installing the system you will be asked to setup WLAN access and authentication. Particular important is setting up the antenna at the location for which is was registered. Setting it up away from this location will reduce the quality of the satellite link significantly. In 50km distance from the registered position we could not establish any stable connection any more. Setup location can be easily changed within your Starlink account, so be sure to do that before transferring the antenna to a new location.
to be gradually extended